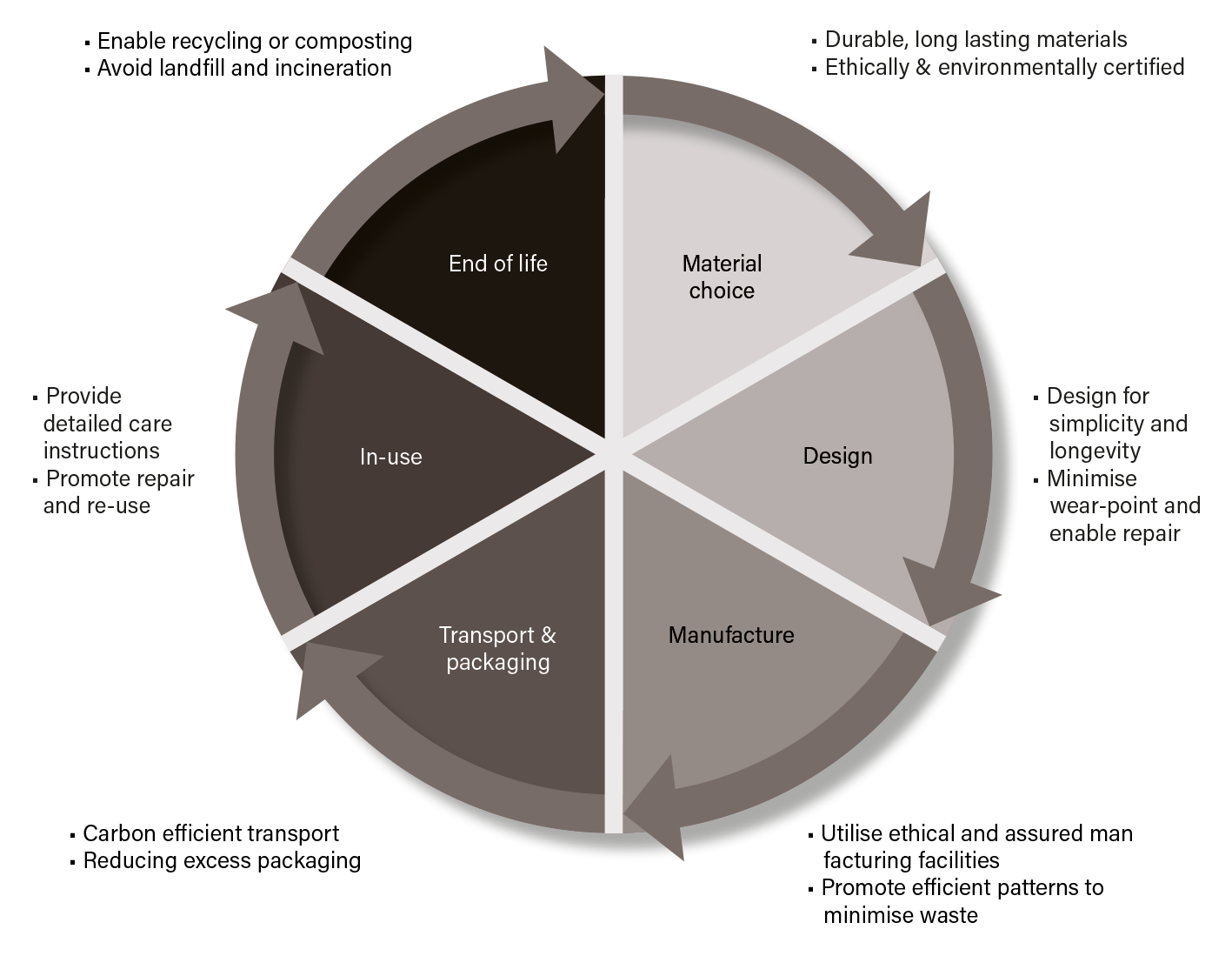
THUMBS-UP SAFETY'S 'CIRCULAR' APPROACH
| Minimum area with visibility material m2 | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Class 1 | Class 2 | Class 3 | |
| Background material | 0.14 | 0.50 | 0.80 |
| Reflective material | 0.10 | 0.13 | 0.20 |
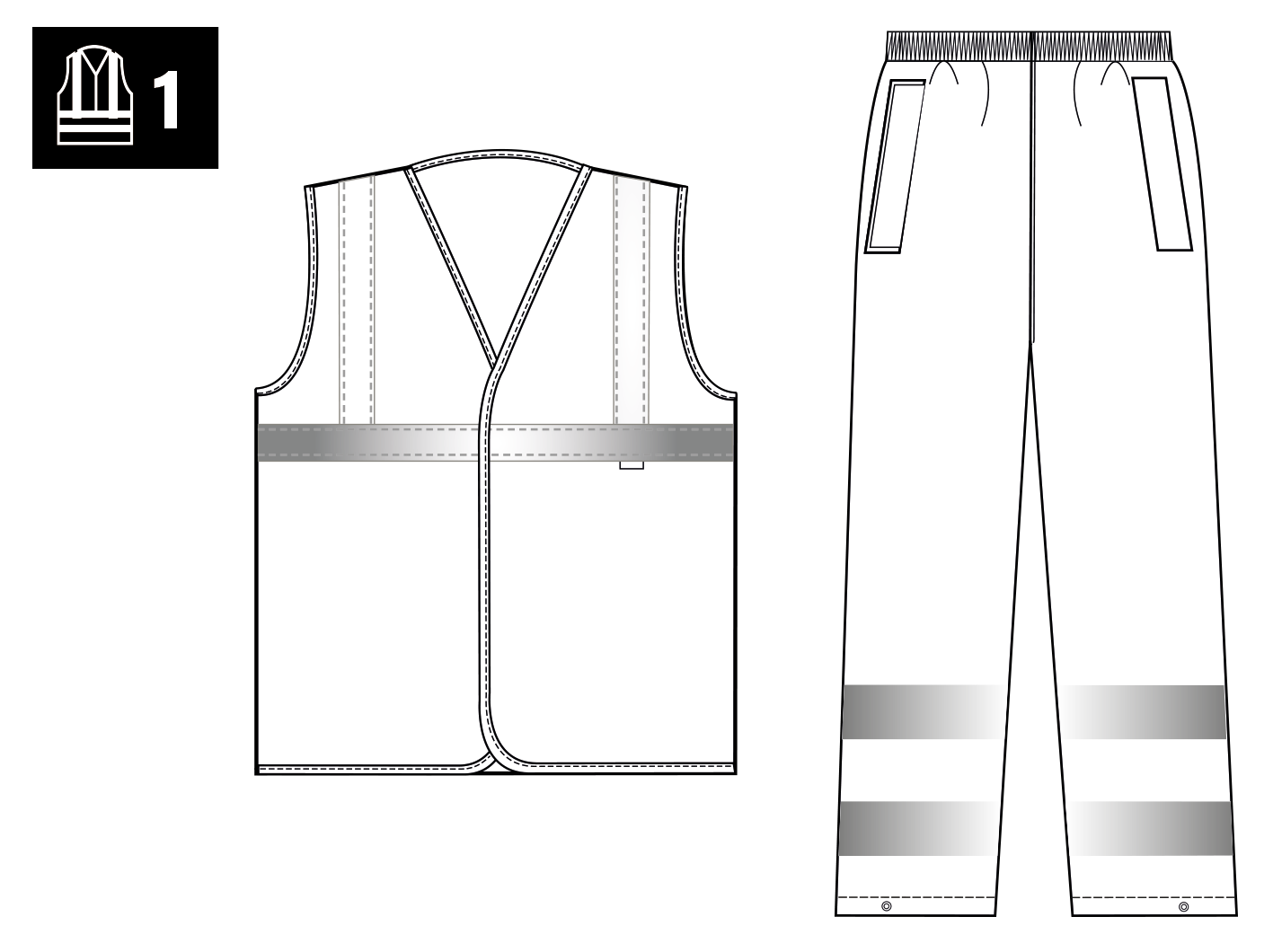
| X - The number next to the graphical symbol indicates the garment class in accordance to Table 1. (max. class 3) | |||
Standards
EN ISO 20471: 2015 High Visibility Clothing Standards
The standard specifies the requirements for high visibility clothing “which is capable of giving a visual signal to the user’s presence”. This now updated standard (from EN471) new has broadened the usage base and a distinction between different types of risk situations has been made. The defined risk situations will be the basis for which norm is applicable for the user. ISO EN 20471 is applicable to high-risk situations. Surface area of fluorescent and retro-reflective material determines the level and performance there are 3 levels.
Minimum Level Minimum level of protection required for any persons working on a private road or to be used in conjunction with a higher classed garment. Must incorporate a minimum of 0.14m2 of background material and 0.10m2 of retroreflective material. (2 metres of 5cm wide reflective tape).
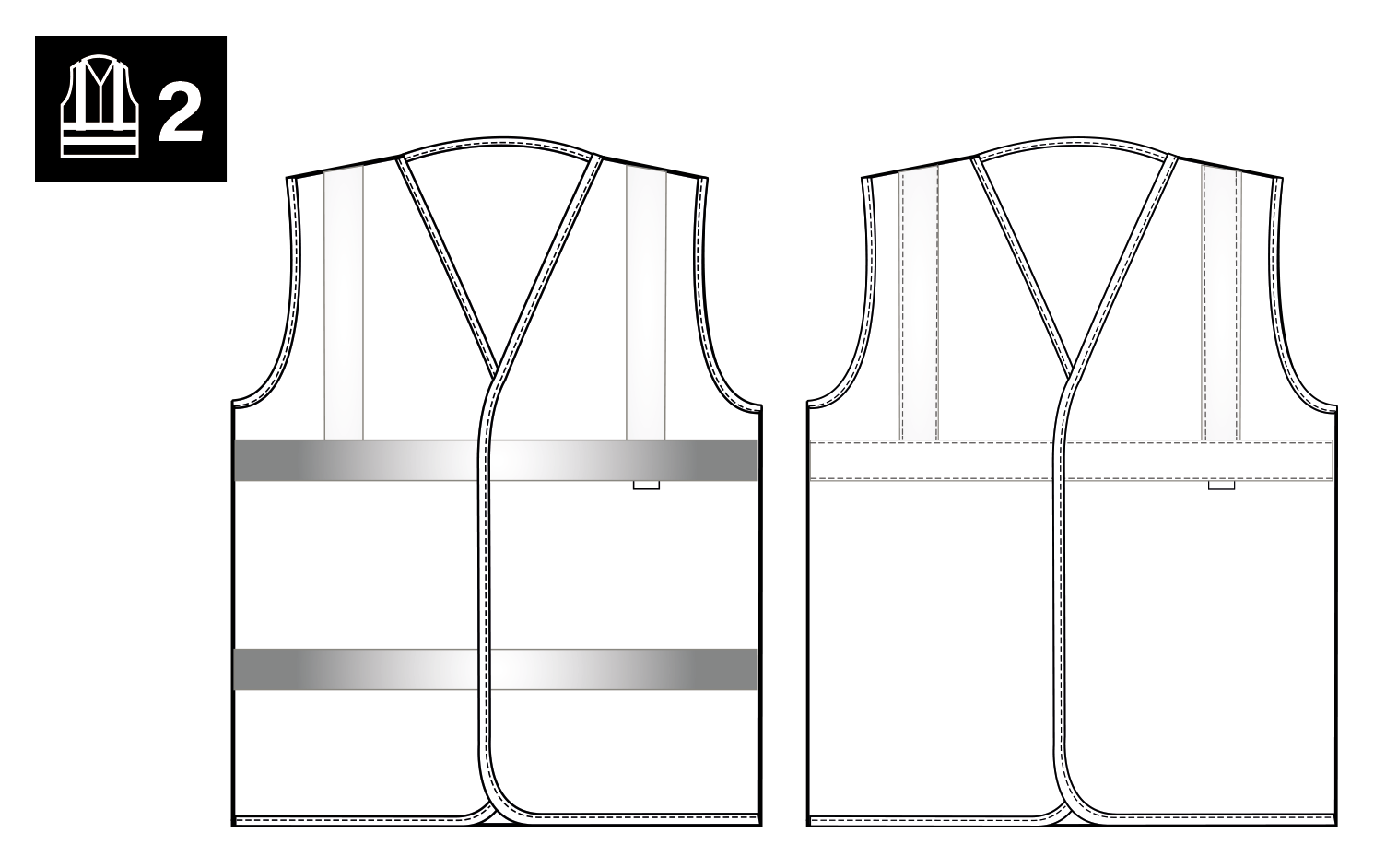
Intermediate Level required for any persons working on or near A and B class roads, also for delivery drivers. Must incorporate a minimum of 0.50m2 of background material and 0.13m2 of retroreflective material. (2.60 metres of 5cm wide reflective tape)
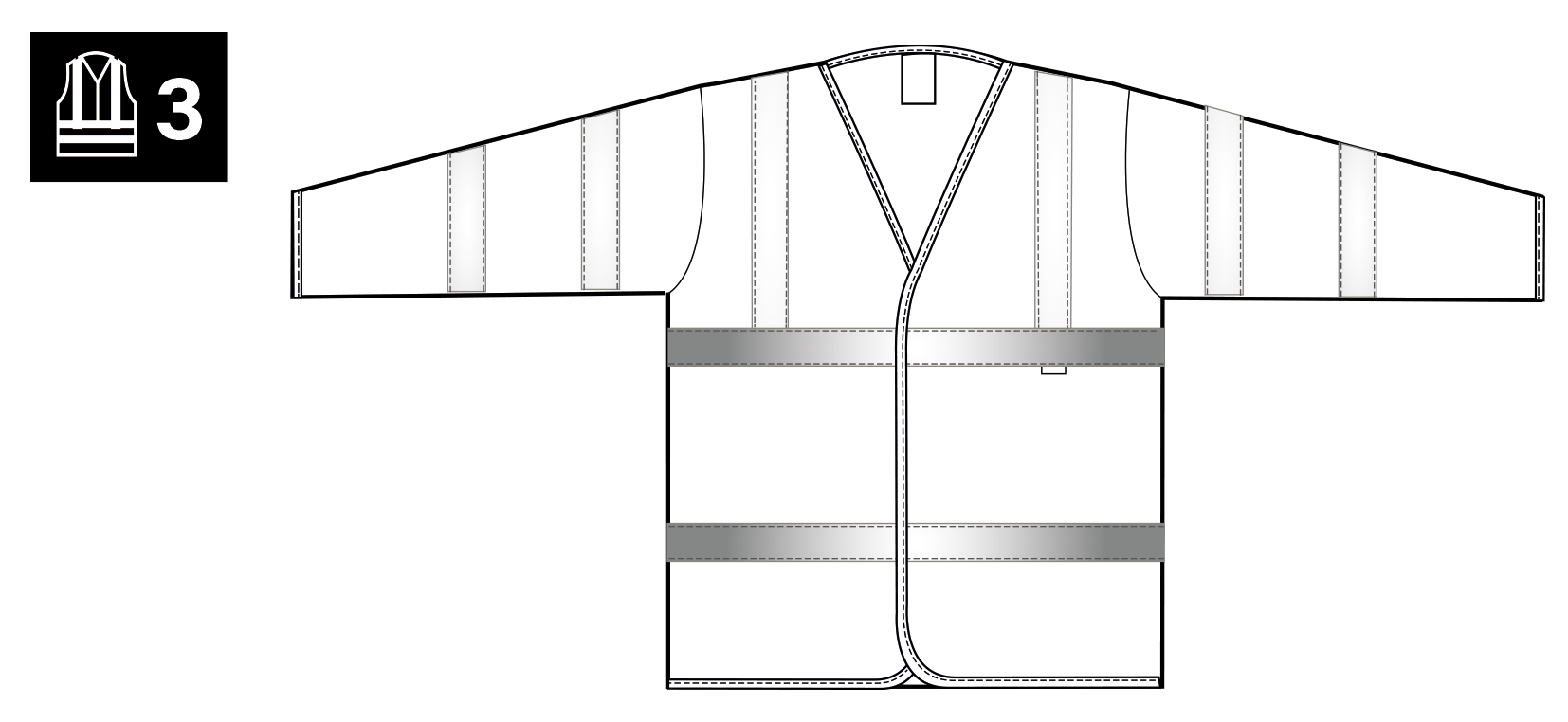
Highest Level Highest level of protection - required for any persons working on or near motorways or dual carriage ways or airports. Must incorporate a minimum of 0.80m2 of background material and 0.20m2 of retro-reflective materials. (4 metres of 5cm wide reflective tape).
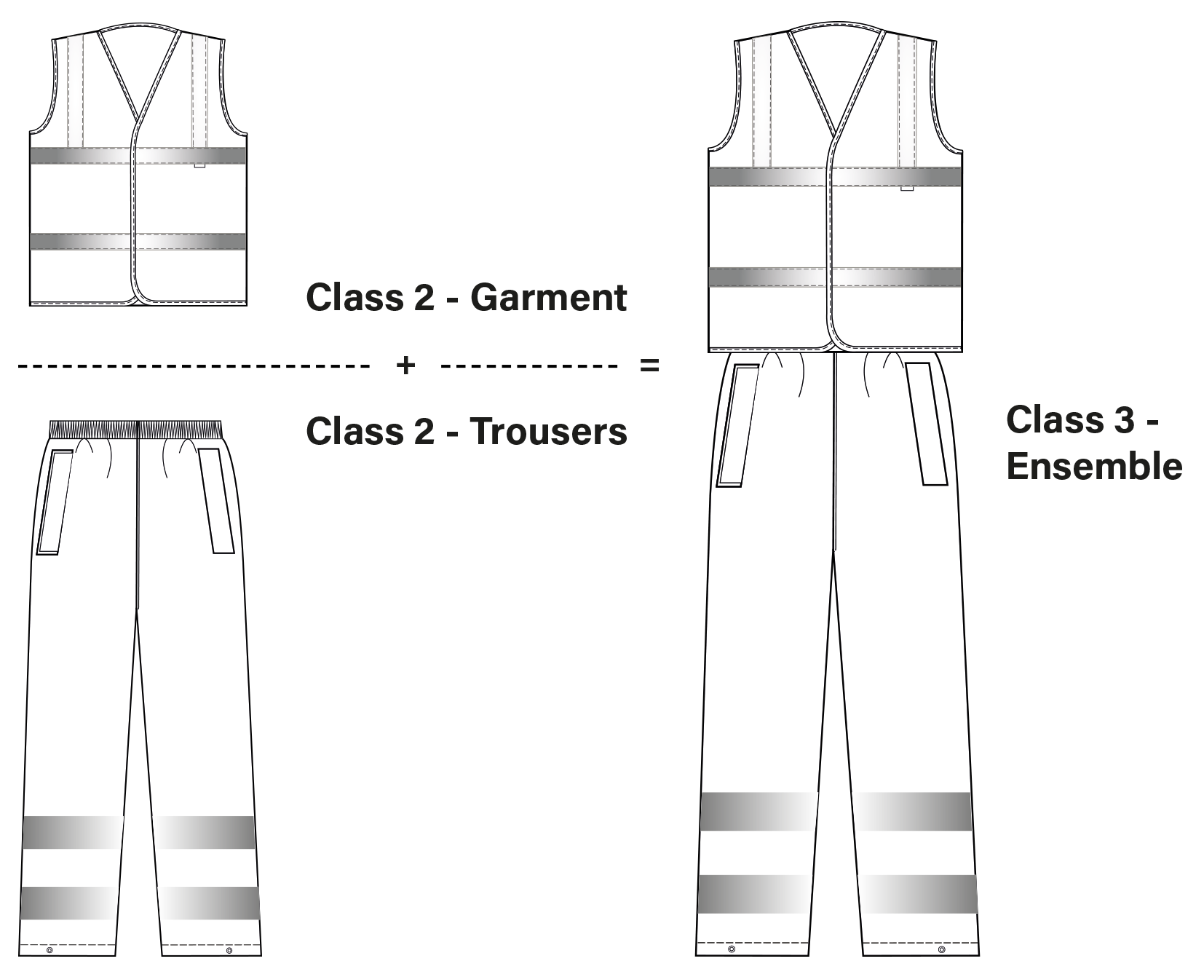
Garment Combinations
The standard also permits this performance class to be met by specifying a single garment or a combination of garments – for instance, a class 2 jacket and a class 2 pair of trousers might be combined and certified as a class 3 combination. Where a combination is specified, this will be deemed to meet the requirements of the standard only when the supplier provides clear instructions on how the classification has been achieved. A class 3 garment is required to cover the torso and have sleeves with reflective bands or/and trouser legs with reflective bands. The area of background or retroreflective material that is covered by badges logos, lettering etc. shall be excluded from the calculation of the required minimum area (unless these additions meet the requirements).
Rail Specific Garment Solutions
The Rail Industry Standards Board (RSSB) published RIS-3279-TOM in December 2016. This will replace GORT3279 Issue 8 as it could not be retained as a National Safety Rule and is therefore reclassified as a Rail Industry Standard which takes effect from April 2017. This standard covers and incorporates the GORT 3279 previously used by the rail industry with little change. New stock post this date will start being marked with the new standards. The Fabric Colour is a specific type of Orange and has to be certified to conform or it cannot be used on UK Railways or surrounds.
| EN 343 - Resistance to Water Penetration | |
|---|---|
| Class 3 | Highest level of foul weather protection |
| Class 2 | Intermediate foul weather protection |
| Class 1 | Lowest level foul weather protection |
| EN 343 - Breathability | |
|---|---|
| Class 3 | Highest level of breathability |
| Class 2 | Intermediate level of breathability |
| Class 1 | Not classified as breathable under the standard |
EN 343:2003 - PROTECTION AGAINST RAIN
Protective clothing certified according to EN 343 protect against precipitation as rain or snow, fog and ground humidity.
Resistance to water penetration and water vapour resistance are the two main properties which are tested in the EN 343. On the label EN 343 will be followed by two numbers. For example, EN343 Class 3:3 The first digit denotes its water penetration resistance, whilst the second digit denotes its breathability.
Please note: EN 343 certified garments will protect the wearer against these conditions provided that:
The garment is closed before use to ensure maximum protective performance.
The fabric is clean. (If it is dirty its performance may be).
The protective clothing is stored in a dry and well ventilated space.
The garment is cared for according to the instructions inside the garment to ensure maximum protective performance.

BS EN ISO 11611:2015 (Replaced EN470-1 1995)
Specifies safety requirements and test methods for protective clothing including hoods, aprons, sleeves and gaiters that are designed to protect the wearer’s body including head (hoods) and feet (gaiters) and that are to be worn during welding and allied processes with comparable risks.

BS EN ISO 11612:2015
Specifies safety requirements and test methods for protective clothing including hoods, aprons, sleeves and gaiters that are designed to protect the wearer’s body including head (hoods) and feet (gaiters) and that are to be worn during welding and allied processes with comparable risks.

BS EN ISO 14116:2015
Specifies safety requirements and test methods for protective clothing including hoods, aprons, sleeves and gaiters that are designed to protect the wearer’s body including head (hoods) and feet (gaiters) and that are to be worn during welding and allied processes with comparable risks.

BS EN 1149-5
Specifies safety requirements and test methods for protective clothing including hoods, aprons, sleeves and gaiters that are designed to protect the wearer’s body including head (hoods) and feet (gaiters) and that are to be worn during welding and allied processes with comparable risks.
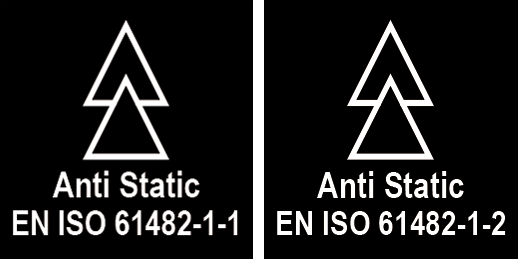
Electric Arc
IEC 61482 Protective clothing against the thermal • hazards of an electric arc • EN61482-1-2:2007 = Arc in the box test method
Class 1 = 4ka • Class 2 = 7ka • EN61482-1-1:2009 = Open Arc test method • ATPV (Arc Thermal Performance Value) cal/cm2
EN ISO 20345:2011 - Safety Ratings

On top of the basic toe protection S1 ensures the footwear has Antistatic protection, is resistant to Fuel, Oil and has energy absorption in the heel.

As S1 above with the addition of a steel or composite midsole offering penetration protection.

S2 has all the same protection as S1 plus the added protection of preventing water penetration and absorption of the upper.

S3 safety footwear encompasses all the same levels of protection as S2 plus midsole penetration resistance.

All the protection offered by S1 but with an entirely moulded polymer/rubber upper (e.g Wellington Boots) making them waterproof and leak proof.

All the same features of S4 footwear with the added benefit of midsole penetration resistance.
Footwear Specification Icons Key

Water Resistant

Anti-static

Penetration Resistant Midsole

Heat Resistant Outsole

Waterproof Membrane

Slip Resistant Outsole A-B-C

Steel Toe Cap

Reinforced Heel

Mono Density Sole

Composite Toe Cap and Midsole

Shoch Absorbing Dual Density Polyurethane Sole

Unisex
SAFETY SLIP RESISTANCE TESTING - CODES: SRA = Slip resistance on ceramic tile floor with Sodium laurel sulphate lubricant. SRB = Slip resistance on steel floor with glycerol lubricant. SRC = Slip resistance on ceramic tile floor with Sodium laurel sulphate lubricant and on steel floor with glycerol lubricant.
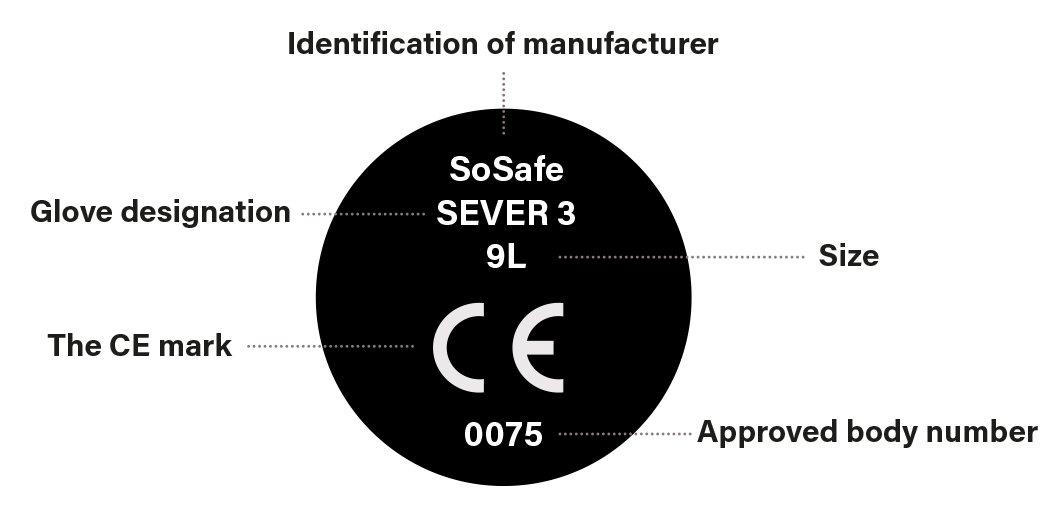
Hand Protection Standards CE Information
The So Safe range of hand protection is manufactured to the highest standards, and is tested independently to meet or exceed the appropriate CE standard for which each product is designed. Backed by our manufacturing partner and enhanced by our own company reputation.
Categorisation
Under the terms of the above directive, gloves fall into the following three categories:
CAT I Simple Design – for minimal risks only. Suitable only for low risk applications where hazards can be identified by the wearer in time to deal with them.
CAT II Intermediate Design – reversible risks. Products are type examined by an approved body where they examine the manufacturers technical specifications and conduct test for the relevant standards to ascertain their conformity and/or performance.
CAT III Complex Design – for protection against mortal danger or risks of irreversible harm. Products are type examined by an approved body as for category II. In addition, the products and manufacturer are subject to EC quality control according to an approved quality system.
Respiratory Protection
EN Standards. All Respiratory Equipment must be tested and carry the CE mark. EN 149. Filtering face piece respirators to protect against particles. Amendment to standard. EN149:2001 + A1:2009. In order to comply with the PPE Directives, it is required that any disposable respirator needs to be tested and marked to the amendments set in 2009. Various levels of protection are available.
| Disposable Respirators | FFP1 | FFP2 | FFP3 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Suitability | Low levels of fine dust, oil or water based mist | Medium levels of fine dust, oil or water based mist | Higher levels of fine dust, oil or water based mist |
European Standards (ENs)
| General Requirements |
|---|
Defines the general requirements for most types of protective gloves, including:
|
| Mechanical Hazards EN388 | |||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |||||||||||||||||||
| Thermal (Heat) Hazards EN407 | |||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |||||||||||||||||||
| Chemical & Micro-Organisms EN374 | ||
|---|---|---|
| EN374-2 Resistance to penetration by mico-organisms. Referred to as acceptable quality level (AQL) | 1-3 | |
| EN374-3 Resistance to chemical hazards - permeation | 1-6 | |
| Protection From Cold EN511 | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||||||||
| When scores are given, the higher the score the better the performance, 0 denotes a fail and X denotes a test. | ||||||||||
 Mon - Fri:9AM-5:30PM
Mon - Fri:9AM-5:30PM