An Introduction to FR Standards
Written By
Thumbs-Up2016.03.26
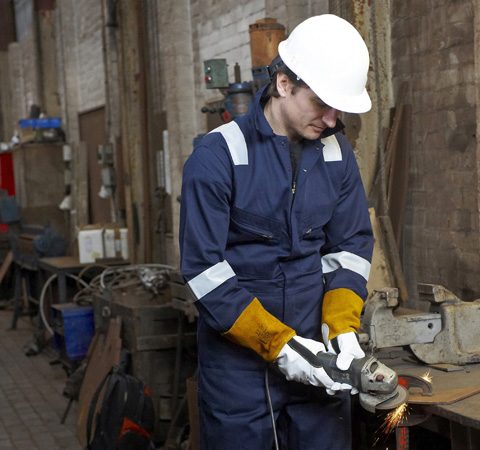

Flame retardant workwear is essential for a whole range of work-based activities including welding and associated processes, and there are a series of international standards in place to ensure that products are suitable for such applications.
Flame retardant clothing that is made is compliant with EN ISO 11611:2007 and EN ISO 11612:2008.
EN ISO 11611:2007
Protective clothing for use in welding and allied processes
This standard covers the assessment of the garment ’s ability to protect against flame and radiant heat. The garment is either awarded Class 1 or Class 2, with Class 1 offering protection against less hazardous welding techniques and situations. In addition to specifying the flame and heat tests performed, this standard includes certain design consideration such as the requirement to cover closures with compliant fabric flaps.
EN ISO 11612:2008
Protective clothing for workers exposed to flame
EN 11612 assesses the convective heat resistance, flame spread and protection against metal splashes offered by the garment. The manufacturer can request certain optional tests according to their requirements, with each test passed denoted by a specific character from A to F (limited flame spread (A1 and A2), protection against convective heat (B), radiant heat (C), molten aluminium splashes (D), molten iron splashes (E) and contact heat (F)). Each character is also accompanied by a level of performance, therefore an article displaying EN ISO 11612:2008 A1+A2 B1 C2 F1 has passed limited flame spread according to both testing procedures detailed within the standard, and has achieved a performance level 1 for convective heat, 2 for molten aluminium splashes and 1 for contact heat. In addition, the standard also dictates certain design characteristics for the garments.
Additional Testing
In addition to EN ISO 11611 and EN ISO 11612, premium flame retardant garments may be tested against standards including IEC 61482-1-2 and EN 1149. IEC 61482-1-2 assesses the level of protection offered by the garment in the event of a electric arc flash, whilst EN 1149 assesses the antistatic protection offered by the product by testing surface resistance, vertical resistance and level of charge decay.
Understandably, all testing is performed on fabric and/or garments that have been pre-treated according to the manufacturers requirements (or a default minimum of 5 wash cycles). This assesses whether or not the garment retains its protective levels during the course of its lifetime in accordance with the stated user instructions.
-
2019-08-08Site safety is one of, if not the, most important aspects of working within the commercial and industrial sector. PPE is intrinsic to safe working practice on site – yet it can often be misused,
-
2019-07-02Thumbs-Up Safety Guide to helping you make the right choices when supplying PPE and workwear Foreward For starters, when it comes to specifying and purchasing PPE products
-
2018-05-18Hazards of varying degrees of severity are present in almost all workplaces – whether its falling objects, moving vehicles, chemicals, noise or a myriad of other dangers.
 Mon - Fri:9AM-5:30PM
Mon - Fri:9AM-5:30PM